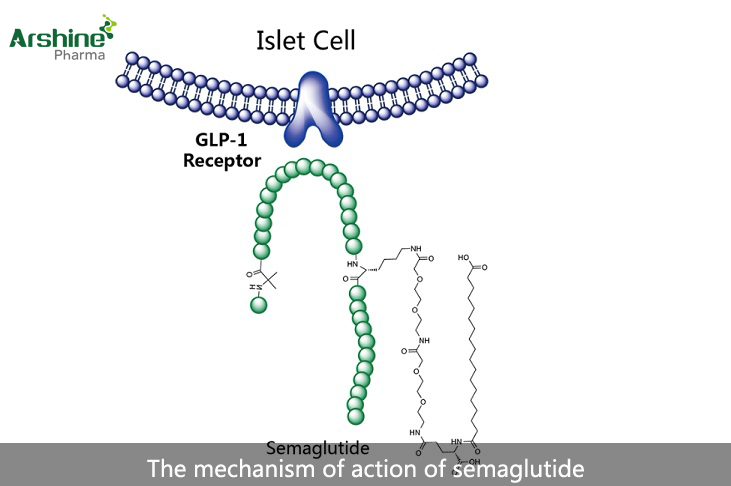
Mechanism of Action of Semaglutide
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It mimics the action of incretin hormones, leading to lower blood glucose levels, increased insulin secretion, inhibited gastrointestinal glucose absorption, and reduced hepatic glucose production. Semaglutide is also being researched for weight management. At higher doses, it has been developed as a treatment for obesity. Clinical trials have shown it to be effective with a high safety profile.
1. Mechanism of Action of Semaglutide – A diabetes treatment that reduces cardiovascular risk and promotes weight loss.
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that can lead to various complications, including cardiovascular disease. In recent years, there has been significant progress in medications for type 2 diabetes, including one named semaglutide. As a GLP-1 receptor agonist, semaglutide is characterized by its ability to lower cardiovascular risk and guide weight loss.
1. Reducing Cardiovascular Risk
Cardiovascular disease is a major risk faced by diabetic patients. Semaglutide lowers cardiovascular risk by activating GLP-1 receptors. GLP-1 receptor agonists increase insulin secretion and decrease glucagon secretion, helping to maintain blood glucose levels within a normal range. Furthermore, semaglutide can reduce body weight and waist circumference while improving insulin resistance. These factors contribute to a reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, making semaglutide widely accepted among diabetic patients.
2. Weight Loss Guidance
Obesity is a common complication of type 2 diabetes and an important issue in diabetes treatment. Semaglutide promotes weight loss by suppressing appetite and reducing food intake. It prolongs gastric emptying time, slowing the absorption of food and increasing feelings of fullness. Additionally, semaglutide enhances thermogenesis and fat oxidation, promoting fat breakdown and combustion, further reducing fat accumulation. These effects enable semaglutide to help diabetic patients improve their physical condition.
3. GLP-1R Agonist
Semaglutide belongs to the category of GLP-1 receptor agonists. GLP-1 is a hormone secreted by intestinal L-cells in response to increased blood glucose, food intake, and gastrointestinal motility. GLP-1 can increase insulin secretion, decrease glucagon secretion, and inhibit insulin release through the activation of GLP-1 receptors. These actions help lower blood glucose levels, improve insulin resistance, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
4. Semaglutide in Treating Type 2 Diabetes
Semaglutide is widely used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes as a GLP-1 receptor agonist. By lowering cardiovascular risk and guiding weight loss, this medication offers significant benefits to diabetic patients. Compared to other medications, semaglutide has pronounced effects and fewer side effects, making it a popular choice in clinical practice. Patients using semaglutide should follow their doctor's guidance and pay attention to the proper use and precautions to ensure safety and efficacy.
As a GLP-1 receptor agonist for treating type 2 diabetes, semaglutide provides new hope through its mechanisms of reducing cardiovascular risk and guiding weight loss. With further research into its action mechanisms, more applications and therapeutic advantages of semaglutide are expected to emerge, offering better treatment options for diabetic patients.
